Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
IUI Treatment at India IVF Center is a simple and cost-effective procedure to help patients conceive a pregnancy, by injecting the best sperm inside the woman’s uterus. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Delhi, Varanasi, India. Intrauterine Insemination IUI.
IntraUterine Insemination is a treatment used for treating infertility. It involves placing male sperm directly inside a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilisation.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that involves placing sperm directly into the uterus to enhance the chances of fertilization. It is a less invasive and less complex procedure compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF), making it a popular choice for couples facing certain fertility challenges. IUI is often recommended for couples with unexplained infertility, mild male factor infertility, or when there is a need to overcome cervical mucus issues. This comprehensive overview will cover the purposes, procedures, success rates, considerations, and potential benefits of Intrauterine Insemination.
Purposes of Intrauterine Insemination:
Unexplained Infertility:
- IUI is frequently used when the cause of infertility is unknown. It provides a targeted approach to increase the chances of sperm reaching and fertilizing the egg within the woman’s reproductive system. Intrauterine Insemination.
Cervical Factor Infertility:
- In some cases, the cervix may produce mucus that hinders the movement of sperm through the reproductive tract. IUI bypasses this potential barrier by placing sperm directly into the uterus. Intrauterine Insemination
Mild Male Factor Infertility:
- When the male partner has a mild decrease in sperm count or motility, IUI can concentrate the sperm and introduce them directly into the uterus, improving the likelihood of reaching the egg. Intrauterine Insemination
Donor Sperm or Same-Sex Couples:
- IUI is commonly used for couples using donor sperm or same-sex couples where one partner provides the egg and the other partner undergoes insemination.
Ovulatory Disorders:
- In cases where the woman has irregular ovulation or ovulatory disorders, IUI can be coordinated with ovulation-inducing medications to enhance the chances of fertilization. Intrauterine Insemination.
The IUI Procedure:
Ovulation Monitoring:
- Before undergoing IUI, the woman’s menstrual cycle is closely monitored to determine the timing of ovulation. This may involve tracking menstrual cycles, using ovulation predictor kits, or undergoing ultrasounds to monitor follicle development.
Semen Collection and Preparation:
- On the day of IUI, the male partner provides a semen sample, or donor sperm is prepared for insemination. The sperm sample undergoes a process called sperm washing, which concentrates healthy and motile sperm, removing non-motile or unhealthy sperm and other impurities.
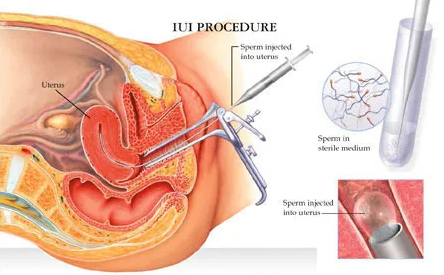
Insemination Procedure:
- The insemination procedure is typically performed in a clinic or fertility center. A speculum is inserted into the woman’s vagina to visualize the cervix. Using a thin catheter, the prepared sperm sample is then introduced directly into the uterus, bypassing the cervix. The entire procedure is relatively quick and does not require anesthesia. Intrauterine Insemination.
Post-Insemination Monitoring:
- After the insemination, the woman may be advised to lie down for a short period to allow the sperm a better chance of reaching the egg. Some clinics may recommend additional monitoring, such as checking progesterone levels or conducting ultrasounds, to assess the success of the procedure.
Success Rates of Intrauterine Insemination:
The success rates of IUI can vary depending on the underlying cause of infertility, the woman’s age, and other factors. On average, the success rates per cycle of IUI range from 10% to 20%, but these rates can increase with multiple cycles. Success rates are influenced by factors such as the quality of the sperm, the woman’s age, and any underlying fertility issues.
Considerations and Potential Benefits:
Cost-Effective:
- In comparison to more complex fertility treatments like IVF, IUI is generally more cost-effective. It involves fewer procedures and less medication, making it a more accessible option for some couples.
Less Invasive:
- IUI is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require surgery or anesthesia. It is considered less stressful and less physically demanding than more invasive fertility treatments.
Lower Risk of Multiple Pregnancies:
- The risk of multiple pregnancies with IUI is lower compared to assisted reproductive technologies like IVF. This may be an advantage for couples who want to minimize the risks associated with carrying multiples.
Addresses Cervical Factor Infertility:
- IUI is particularly beneficial for couples facing cervical mucus issues or other factors that impede natural sperm transport. By placing sperm directly into the uterus, IUI circumvents these obstacles.
Can Be Used with Ovulation-Inducing Medications:
- IUI can be combined with ovulation-inducing medications, such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins, to stimulate the development of multiple eggs. This can further increase the chances of conception.
Limitations and Considerations:
Success Rates Compared to IVF:
- While IUI can be effective for certain fertility challenges, it generally has lower success rates compared to IVF, especially for couples with more complex infertility issues.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS):
- In cases where ovulation-inducing medications are used in conjunction with IUI, there is a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This condition can cause the ovaries to become swollen and painful.
Male Factor Infertility Limitations:
- IUI may not be as effective in cases of severe male factor infertility where sperm quality and quantity are significantly compromised.
Unexplained Infertility Challenges:
- IUI may not always be successful in cases of unexplained infertility where the cause remains unclear, and multiple IUI cycles may be needed to achieve pregnancy.
Conclusion:
Intrauterine Insemination is a valuable fertility treatment that offers a less invasive and more accessible option for couples facing certain fertility challenges. Its success depends on various factors, and its appropriateness should be discussed with a fertility specialist based on the specific circumstances of each couple. While IUI may not be suitable for all cases of infertility, it has provided hope and success for many couples on their journey to achieving a healthy pregnancy and building a family. As with any fertility treatment, open communication with healthcare providers, understanding potential risks and benefits, and realistic expectations are crucial components of the decision-making process.
